Pritzker lays out big plans while citing strong fiscal picture
By Jerry Nowicki Capitol News Illinois — February 15, 2023
Gov. J.B. Pritzker delivers his state budget address Wednesday, Feb. 15 from the Illinois House chamber in Springfield. (illinois.gov)
SPRINGFIELD – Gov. J.B. Pritzker proposed a state budget Wednesday, Feb. 15 that anticipates continued strong revenue receipts even as federal COVID-19 stimulus funds dry up, allowing for increased spending across all levels of education and most of state government.
Giving his annual speech from the state House chamber for the first time since the COVID-19 pandemic upended daily life across the globe, the governor asserted that the actions of his first term laid the groundwork for the new spending he outlined Wednesday.
“Fiscal responsibility isn’t easy, nor is it a one-time fix,” Pritzker said. “It’s an annual effort that requires persistence. It requires conservative revenue estimates, as all of my budget proposals have. But when done right, consistent balanced budgets strengthen the institutions our residents rely upon, creates new opportunities for success, and makes life easier for the people of Illinois.”
All told, the governor outlined a Fiscal Year 2024 budget that anticipates $49.9 billion in general revenues, a $1.4 billion decrease from current FY 23 estimates. Excluding current-year contributions to the state’s “rainy day” fund, the $49.6 billion in approved FY 24 spending represents a drop-off of about $350 million.
New spending
Much of the spending growth proposed by Pritzker would remain on the books beyond Fiscal Year 2024, unlike recent one-time spending approved over the past two budget years.
The spending plan allocates a $250 million funding increase to expand child care, a more-than $500 million increase for K-12 education-related spending, and a combined $200 million for state college operations and low-income scholarships.
The governor also proposed adding $54.6 million from the General Revenue Fund to the Department of Children and Family Services budget for provider rate reforms, programs to protect workers and boosting staffing by 192 new hires.
 The plan also ups the GRF contribution to the Department of Human Services by more than $650 million, a number that includes some of the new early childhood spending.
The plan also ups the GRF contribution to the Department of Human Services by more than $650 million, a number that includes some of the new early childhood spending.
The Department of Healthcare and Family Services, meanwhile, would see an increase of more than $700 million in GRF spending.
“The investments we’ve made in social service agencies over the past four years and that we are proposing for the coming year will finally have reversed the hollowing out that occurred in human services under the previous administration if we are able to hire up enough staff in this tight labor market,” Pritzker said. “We are cautiously optimistic that we can do so.”
The spending increases sparked concern from Republicans as the proposal heads to lawmakers in the General Assembly for their consideration over the next several months.
“Last year, the Democratic majority added another $4 billion in spending on top of the governor’s proposed budget. This year, the governor’s proposal seeks to build upon that spending,” Senate Minority Leader John Curran said in a statement. “We must heed the warnings of Comptroller (Susana) Mendoza and be disciplined in our fiscal approach at a time when we are likely to experience a recession.”
Mendoza, meanwhile, told Capitol News Illinois on Wednesday that after seeing Pritzker’s proposal, she was supportive of the new spending, which she called “strategic, targeted” investments in the state’s future.
Increased deficit?
In announcing some of the new spending in a media call Tuesday, Pritzker downplayed the potential that it could lead to a deficit in future budget years.
The Governor’s Office of Management and Budget predicted in November that by 2025, Illinois could be facing a deficit of up to $384 million, potentially increasing in the following years.
“I’ve been working very hard to make sure that we’re not going to have deficits going forward,” Pritzker said. “And it appears that we’re doing better than expected.”
 While senior budget officials declined to give an updated revenue projection for FY 2025 in a briefing prior to the budget address, they noted that the current-year budget isn’t reliant on “one-time” revenues.
While senior budget officials declined to give an updated revenue projection for FY 2025 in a briefing prior to the budget address, they noted that the current-year budget isn’t reliant on “one-time” revenues.
And their $49.9 billion revenue projection factored in a “mild recession” that could occur this year, they noted.
Still, the appropriated spending remains relatively close to the past two years, indicating a level of confidence that the economy will at least temporarily continue to perform at a pace that budgeting forecasters had previously characterized as “amazing” amid pandemic-related stimulus.
Individual income tax revenues are expected to grow by $778 million in FY 24 while corporate income tax revenues shrink by $175 million. Sales taxes and all other sources are expected to remain relatively level, while the only major decrease – of nearly $1.3 billion – comes in the category of “transfers in.” That’s because strong income tax performance in FY 22 created a $1.4 billion transfer into the general fund for the current year that isn’t expected to repeat. (Illinois Fiscal year 2024 Budget Outline)
Drivers of ‘new’ revenue
In a media briefing Tuesday, Pritzker chalked up the strong revenue performance at least partially to a number of laws signed in his first term. Those included eliminating certain corporate tax exemptions to raise about $655 million annually and streamlining collection of online sales tax to increase revenue collections by hundreds of millions as well. He also cited general revenue transfers from recreational marijuana taxes as helping make budgeting easier.
But Pritzker cited another “new” revenue source made available by recent state actions – general funds that are no longer going to interest payments because the source of debt has been repaid.
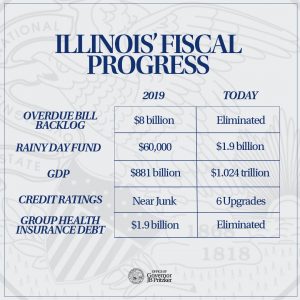
“As of Fiscal Year 2023, all our state’s short-term and medium-term liabilities will have been eliminated. All of it,” Pritzker said in his speech. “Our budgets are built on a solid foundation of normalized state revenue and more efficient management of state resources.”
He specifically noted the state paid down $900 million in group health insurance debt, $230 million in College Illinois debt, $4.5 billion in borrowing to keep the Unemployment Trust Fund afloat and $1.3 billion in previous interfund borrowing.
Pritzker’s office estimated that nearly $3 billion in savings to the state’s coffers has been realized through the early debt repayment and other debt refinancing, a pension buyout program, changes to collective bargaining for state employee health insurance costs and other actions.
In the FY24 budget, the governor proposed allocating $450 million to defease debt taken on through the Railsplitter Tobacco Settlement Authority to pay bills during the Great Recession. It could save an estimated $60 million in interest.
Pritzker also proposed using an updated current-year surplus to contribute an additional $200 million to the state’s pension fund beyond the amount required in law. That would bring the total pension liability savings resulting from recent changes to law to $4 billion, although the state’s unfunded pension liability remains at roughly $139 billion.
“We have used our surpluses to chip away at our long-term liabilities too, including $500 million more into our pension stabilization fund over the last two years and my proposal this year to increase that by another $200 million,” Pritzker said. “The percent of the budget needed to meet our statutory obligations has declined as our revenues have grown and our fiscal fortunes have improved.”
jnowicki@capitolnewsillinois.com







