State’s pension debt grows to $139.7 billion
By Peter Hancock Capitol News Illinois — December 12, 2022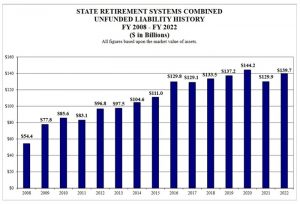
Unfunded liabilities in Illinois’ five pension funds grew 7.5 percent, to $139.7 billion, in the fiscal year that ended June 30. (Credit: Commission on Government Forecasting and Accountability)
SPRINGFIELD – Illinois’ unfunded pension liability grew by $9.8 billion, or 7.5 percent, in the fiscal year that ended June 30, due in large part to market losses in a volatile economy.
The Commission on Government Forecasting and Accountability reported Thursday that the total unfunded liability in the state’s five pension funds reached a total of $139.7 billion, leaving them with a funded ratio of just 44.1 percent.
Those numbers are based on an annual report from the state actuary, who reviews the preliminary financial data submitted by each of the five funds.
The funded ratio reflects the difference in the market value of the funds’ assets and the amount of money the funds would need to immediately pay all members the full amounts of benefits they are owed for the rest of time.
Although that’s an important measure of the systems’ long-term financial health, it does not reflect their current ability to pay out benefits that are owed. All five of the pension funds continue to pay out benefits to eligible retirees on a timely basis.
All told, the five pension funds had combined liabilities of $248.8 billion June 30 and total assets of $109.1 billion.
Of the five funds, the Illinois Teachers Retirement System, which is the state’s largest pension fund, showed the strongest performance, losing only 1.2 percent of its market value. In a statement Wednesday, TRS said the median rate of return among large pension systems during the year was -7.6 percent.
The State University Retirement System lost 1.4 percent of its value. The State Employee Retirement System, Judicial Retirement System and General Assembly Retirement System all saw market value losses greater than 6 percent.
Pension systems generally receive funding from three sources – employee contributions; employer contributions; and returns on investments. The large unfunded liability in Illinois’ pension funds is the result of the state failing for decades to make adequate contributions as the employer.
In 1994, then-Gov. Jim Edgar, a Republican, pushed through legislation whereby the state would gradually increase its contributions over the next 50 years until the funding ratio would reach 90 percent by 2045, a plan commonly referred to as the “Edgar Ramp.”
But the state has not always met its targets under that plan. In 2005, lawmakers passed a bill allowing reduced contributions, known as “pension holidays,” in times of budgetary pressure. As a result, contributions in 2006 and 2007 were roughly $1 billion lower than the amounts required under the Edgar Ramp.
The financial crisis in 2007-2008 that led to the Great Recession also resulted in significant losses for the pension funds.
Since taking office in 2019, Democratic Gov. JB Pritzker has included full funding at the statutorily required levels in each of his budgets, and over the past two fiscal years authorized an additional $500 million above what was required by law, bringing the total amount paid in to just under $11 billion, including $9.9 billion from the General Revenue Fund.
Under the 1995 law, each of the funds is required to submit a certification prior to Nov. 1 stating how much the state needs to contribute the following fiscal year.
According to those reports, COGFA said, preliminary estimates show the required contributions for the upcoming fiscal year will total $10.9 billion, including $9.8 billion from general revenues. Even that, however, would be far short of what it would take to cover the actual costs that the funds will accrue during the year.
The “actuarily determined contributions” for the five funds – the amount the state would be obligated to pay, even if the systems were 100-percent funded – would be $15.4 billion.
phancock@capitolnewsillinois.com







