Deer ticks still a concern with warm winter
Chronicle Media — January 10, 2019The mild weather beginning to 2019 has been seen as a real positive to many people, but there are drawbacks to not having cold, below freezing conditions we typically associate with this time of year.
On Jan. 4, the Kendall County Health Department collected a deer tick, a known carrier of Lyme disease. Ticks are out when weather is over 40ᵒ F.
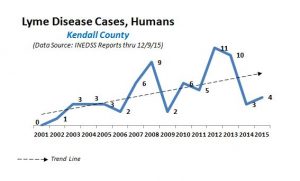
Cases of Lyme Disease have been on the rise over the past five years in Kendall County.
Although at least 15 species of ticks occur in Illinois, only a few of these ticks are likely to be encountered by people: American dog tick, lone star tick, blacklegged (deer) tick, brown dog tick and winter tick.
In Illinois, the adult American dog ticks are most active in April, May and June. By September, the adults are inactive and are rarely observed. The American dog tick can transmit Rocky Mountain spotted fever, tularemiaand possibly ehrlichiosis to humans.
The lone star tick is most active from April through the end of July. Although it can transmit Rocky Mountain spotted fever, the lone star tick is not as likely to transmit the disease as the American dog tick. This tick may also transmit tularemia and ehrlichiosis to humans.
The blacklegged (deer tick) can transmit Lyme disease and possibly ehrlichiosis to humans. The deer tick has been found sporadically in many Illinois counties. However, in recent years it has been common only in limited areas, mostly in northern Illinois.
 Deer ticks may carry Lyme disease which can be serious if left untreated. In 75 percent of the cases, a red circular rash develops at the site of the bite. Flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, and aching joints may occur and reoccur for several weeks.
Deer ticks may carry Lyme disease which can be serious if left untreated. In 75 percent of the cases, a red circular rash develops at the site of the bite. Flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, and aching joints may occur and reoccur for several weeks.
If not treated, irregularities in heartbeat, nervous system problems and arthritis may develop. Antibiotics are effective in controlling this disease if treatment is started early.
For more information, visit the Kendall County Health Department Facebook page, www.facebook.com/kendallhealth/, or the the web site at http://www.kendallhealth.org.